Prof. Minkyu Joo proposes a method for evaluating 2D electronic materials using machine learning
- Views 7129
- Writer 커뮤니케이션팀
- 보도일자 2021-02-05
Professor Minkyu Joo of the Department of Applied Physics introduced machine learning to evaluate the noise characteristics of low-frequency currents of two-dimensional electronic materials, and proved that it is possible to quickly and accurately classify electronic materials and evaluate various properties.
This research was supported by the young researcher support program hosted by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the bilateral research exchange support project (France), and the research results were published on December 13 in npj 2D Materials and Applications (IF = 9.324).
(Title of paper: Multiple machine learning approach to the inference of two-dimensional nanoelectronic materials via featurization of charge fluctuation interference)

According to Professor Joo, machine learning and deep learning-based data analysis methods are new approaches that can improve the accuracy and speed of data analysis, and are recently being applied to various applications such as medicine, image recognition, voice search, and molecular/material science.
The joint research team of Prof. Joo and Professor Gyutae Kim of Korea University applied these advantages of machine learning and deep learning to the analysis of the noise characteristics of low-frequency currents in electronic materials, and succeeded in non-destructively identifying the cause of electric charge scattering resulting from the crystallinity of electronic materials, lattice vibration, surface trap distribution, and channel and insulating material defects.
In particular, the hidden-Markov model-based real-time neural network approach was applied to machine learning and deep learning, and based on this, the types of 2D electronic materials, gate dielectrics, contact metals, presence or absence of doping, defect density, and Coulomb scattering parameters were extracted with high accuracy from the low-frequency noise characteristics of 2D electronic materials acquired in various environments. (See figure).
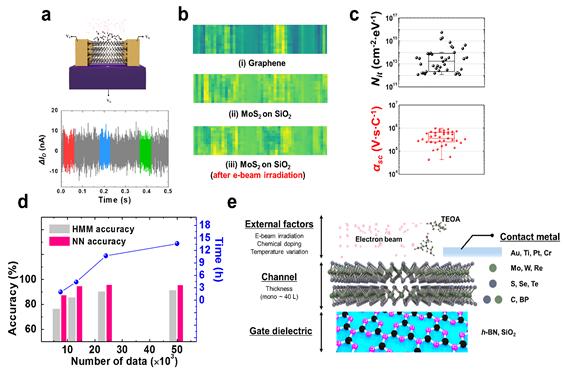
Professor Joo said, "The high learning flexibility of this study is expected to be very useful in discriminating factors that degrade the performance and reliability of various electronic materials, and suggesting optimized manufacturing conditions and structures."



